Array.prototype.fill
fill
作为 JavaScript 中数组的一个方法,fill 可以用指定的值填充数组中的元素。它具有以下含义:
动词:填满、充满、装满、堵塞、填补、满足、担任、耗去、吃饱、按订单供应。
名词:填满的量、足够的量、吃饱的量、喝足的量。
参数
fill 方法接受三个参数:填充值、开始下标和结束下标。
- 填充值:用于填充数组的值。
- 开始下标(可选):开始填充的位置,默认为 0。如果为负数,则从数组末尾倒数计算。
- 结束下标(可选):结束填充的位置(不包含该位置),默认为数组长度。如果为负数,则从数组末尾倒数计算。
示例
const arr = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
// 填充区间 [2,4)
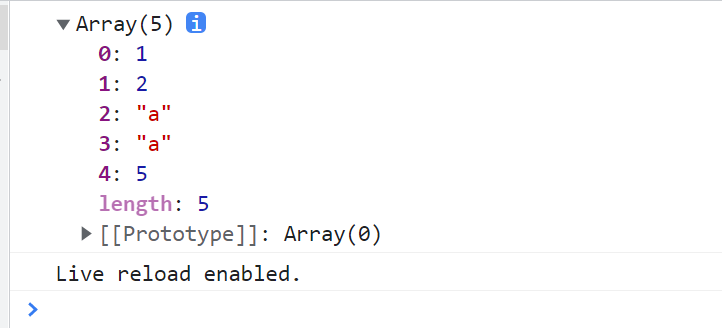
const newArr = arr.fill('a', 2, 4);
console.log(newArr); // [1, 2, 'a', 'a', 5]
// newArr 返回的是原数组的引用
console.log(arr === newArr); // true
// 全部覆盖,使用默认参数
const newArrUn = arr.fill();
console.log(newArrUn); // [undefined, undefined, undefined, undefined, undefined]
// start 非数字,end 为数字 [0,4)
const arr1 = arr.fill('g', 'a', 4);
console.log(arr1); // ['g', 'g', 'g', 'g', undefined]
// 未定义 start 和 end,全部覆盖
const arr2 = arr.fill('g', undefined, undefined);
console.log(arr2); // ['g', 'g', 'g', 'g', 'g']
数组转类数组
在某些情况下,我们可能需要将数组转换为类数组对象。类数组对象具有数组的一些特性,如 length 属性和索引,但不具备数组的所有方法。以下是一个将数组转换为类数组对象的示例:
function makeArrayLike(arr) {
const arrLike = {
length: arr.length,
push: Array.prototype.push,
splice: Array.prototype.splice,
};
arr.forEach((item, index) => {
Array.prototype.fill.call(arrLike, item, index, index + 1);
});
return arrLike;
}
const newObj = makeArrayLike(['a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e', 'f']);
console.log(newObj);
// { '0': 'a', '1': 'b', '2': 'c', '3': 'd', '4': 'e', '5': 'f', length: 6, push: [Function: push], splice: [Function: splice] }
在上述代码中,我定义了一个 makeArrayLike 函数,它接收一个数组并返回一个类数组对象。通过使用 Array.prototype.fill 方法,我将数组的每个元素填充到类数组对象中对应的位置。
实现 fill
为了更好地理解 fill 方法的工作原理,以下是一个自定义实现 fill 方法的示例:
Array.prototype.myFill = function (value, start, end) {
// 设置填充值,如果未提供则为 undefined
const fillValue = typeof value !== 'undefined' ? value : undefined;
// 转换 this 对象为数组
if (this == null) {
throw new TypeError('Cannot convert undefined or null to object');
}
const obj = Object(this);
const len = obj.length >>> 0;
// 计算开始索引
let startIndex = typeof start === 'undefined' ? 0 : Number(start);
startIndex = isNaN(startIndex) ? 0 : startIndex < 0 ? Math.max(len + startIndex, 0) : Math.min(startIndex, len);
// 计算结束索引
let endIndex = typeof end === 'undefined' ? len : Number(end);
endIndex = isNaN(endIndex) ? len : endIndex < 0 ? Math.max(len + endIndex, 0) : Math.min(endIndex, len);
// 填充数组
for (let i = startIndex; i < endIndex; i++) {
obj[i] = fillValue;
}
return obj;
};
const arr = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
const newArr = arr.myFill('a', 2, 4);
console.log(newArr); // [1, 2, 'a', 'a', 5]
在这个实现中,我扩展了 Array.prototype 添加了一个 myFill 方法。该方法首先验证 this 是否为有效的数组对象,然后计算开始和结束索引,最后在指定范围内填充值。
通过这个示例,可以更深入地理解 fill 方法的内部工作机制,并了解如何在实际开发中自定义数组方法。