初始化参数
在函数执行期间,参数的默认赋值是undefined。
function test(a, b) {
console.log(a);
console.log(b);
}
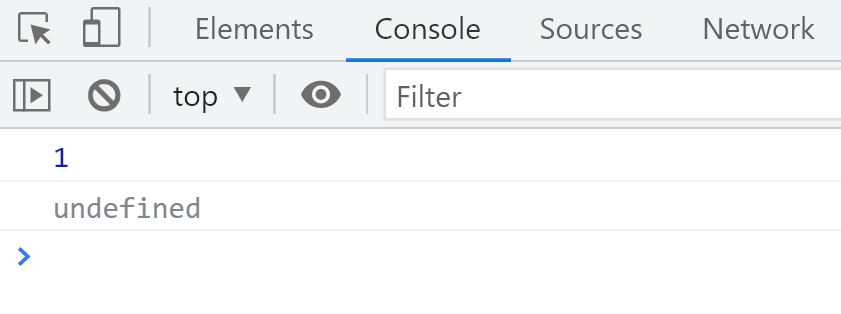
test(1);
结果
默认值
function test(a = 1, b) {
console.log(a);
console.log(b);
}
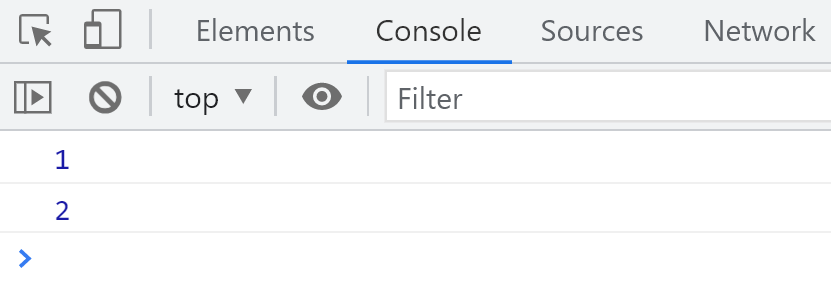
test(undefined, 2);
结果
function test(a = undefined, b) {
console.log(a);
console.log(b);
}
test(1, 2);
结果

function test(a, b) {
console.log(a);
console.log(b);
}
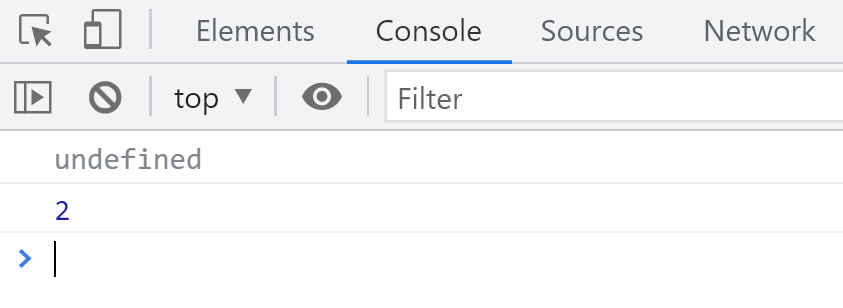
test(undefined, 2);
结果
总结
只要参数不是undefined就使用传入的值,如果都是undefined就打印undefined。
如何给参数赋默认值
如果实参没传就使用后面的值,相当于给参数一个默认值。
function test(a, b) {
var a = arguments[0] || 1;
var b = arguments[1] || 2;
console.log(a + b);
}
test(3, 4);
上述写法存在一个问题,如果传入的值不是undefined而是其他falsy值,会被隐式转换,导致||后面的值被使用。
function test(a, b) {
var a, b;
if (typeof arguments[0] !== 'undefined') {
a = arguments[0];
} else {
a = 1;
}
if (typeof arguments[1] !== 'undefined') {
b = arguments[1];
} else {
b = 2;
}
console.log(a + b);
}
test(0, 0);
使用if配合typeof可以准确判断undefined,避免程序出现问题。
function test(a, b) {
var a = typeof arguments[0] !== 'undefined' ? arguments[0] : 1;
var b = typeof arguments[1] !== 'undefined' ? arguments[1] : 2;
console.log(a + b);
}
test('', 1);
通过三元表达式检测typeof来赋默认值。
预编译
JavaScript引擎的工作流程
语法分析,由上至下,从左到右检查语法错误。
预编译阶段。
解释执行,一行一行地解释和执行代码。
两个现象
test();
function test() {
console.log(1);
}
正常打印1
console.log(a);
var a = 10;
console.log(b);
var b;
打印undefined
总结
函数声明会被提升到整个代码的顶部。
变量只有声明会被提升,赋值不会被提升。
隐式全局变量
隐式全局变量
// var a =1;
a = 1;
console.log(a);
上述代码,无论是否使用var,都会正常打印1。这是因为未声明变量会自动成为全局变量。
var a = 1;
b = 2;
console.log(a);
// window.a 也可以正常打印
console.log(window.a);
// 因为不论是否使用var,变量都属于Window对象
window = {
a: 1,
b: 2,
};
即a === window.a,所有全局变量都属于Window对象。
// 全局变量
var a = 1;
// 隐式全局变量
b = 2;
console.log(a);
console.log(window.a);
特性
function test() {
var a = (b = 1);
}
test();
console.log(b);
在函数内部没有声明变量b,因此b被提升到全局Window对象。
function test() {
var a = (b = 1);
}
test();
// console.log(a);
console.log(window.a);
为什么 console.log(a); 报错而 console.log(window.a); 打印undefined
因为a在全局作用域中未定义,而window.a尝试从Window对象中查找,未找到则返回undefined。
函数预编译做了什么
AO
Activation Object 函数上下文,针对函数
创建AO对象。
AO= {
}
查找函数的形参和变量声明,作为AO的属性,初始值为undefined。
将实参值赋给形参。
查找函数声明,并赋值函数体。
执行函数。
例一
function test(a) {
console.log(a);
var a = 1;
console.log(a);
function a() {}
console.log(a);
var b = function () {}
console.log(b);
function d() {}
}
test(2);
AO = {
a: undefined
-> 2
-> function a() {}
-> 1,
b: undefined
-> function () {}
d: function d() {}
}
例二
function test(a, b) {
console.log(a);
c = 0;
var c;
a = 5;
b = 6;
console.log(b);
function b() {}
function d() {}
console.log(b);
}
test(1);
AO{
a: undefined,
->1
->5
b: undefined,
->function b() {}
->6
c: undefined,
->0
d: function d() {}
}
GO
Global Object 全局上下文
GO 等同于 Window
创建GO对象。
GO{
}
查找变量声明,赋值为undefined,GO 没有参数
查找函数声明。
按顺序执行代码。
console.log(a,b);
function a(){}
var b = function(){}
GO{
b: undefined
a: function a(){}
}
function test(){
var a = b =1;
console.log(a);
}
test();
GO{
b:1
}
AO={
a: undefined ->1
}
var b = 3;
console.log(a);
function a(a) {
console.log(a);
var a = 2;
console.log(a);
function a() {
var b = 5;
console.log(b);
}
}
a(1);
GO{
b: undefined
-> 3
a: function a(){...}
}
AO{
a: undefined
->1
-> function a() {
}
2
b: undefined
->5
}
AO中存在变量时,不会去GO中查找。
a = 1;
function test() {
// AO中有a,不去GO中查找
console.log(a);
a = 2;
console.log(a);
var a = 3;
console.log(a);
}
test();
GO{
a: undefined
1
test: undefined
}
AO{
a: undefined
undefined
2
3
}
使用var声明的变量作用域为当前作用域,直接声明为全局变量。
function test() {
console.log(b);
if (a) {
var b = 2;
}
c = 3;
console.log(c);
}
var a =1;
test();
a = 1;
console.log(a);
GO{
a: undefined
1
test: function test(){}
c: 3
}
AO{
b: undefined
}
练习
var a = false + 1;
console.log(a);
// false 隐式类型转换为 0,结果为 1
var b = false == 1;
console.log(b);
// 比较运算输出布尔值类型,结果为 false
// 字符串的 undefined 是 true,-true = -1,+undefined = NaN
if (typeof a && -true + +undefined + '') {
console.log('通过');
} else {
console.log('未通过');
}
console.log(typeof a);
// 字符串 '3' 隐式转换成 number
if (1 + 5 * '3' === 16) {
console.log('通过了');
} else {
console.log('未通过');
}
// 1 + 0 - 0 = 1,不往后执行
console.log(!!' ' + !!'' - !!false || '未通过');