Java 异常处理指南
异常与错误的本质区别在于异常通常可以被程序处理,而错误则是程序无法处理的严重问题。在编写代码时,笔者关注如何处理异常,而不是试图捕获和处理错误。
Throwable 类
这是 Java 异常层次结构的根类。所有错误和异常都是此类的子类。Throwable 提供了常用的方法,如 getMessage()、toString() 和 printStackTrace(),用于获取异常信息和堆栈跟踪。
Exception 类
这是所有可检查异常的基类。可检查异常必须被捕获(catch)或声明抛出(throws)。Exception 类继承自 Throwable 类,确保程序能够适当地处理这些异常。
RuntimeException 类
这是所有运行时异常的基类。运行时异常不需要捕获或声明抛出,通常表示编程错误。RuntimeException 类继承自 Exception 类,常见于逻辑错误或不合理的假设。
Error 类
这是所有错误的基类。错误通常在正常操作中不会出现的严重问题,例如 OutOfMemoryError。Error 类也继承自 Throwable 类,表示虚拟机无法恢复的状态。
各种具体的异常类
IOException
IOException 表示发生 I/O 错误时抛出的异常。这是一个非常通用的异常类,用于处理与输入/输出相关的问题。
try {
FileInputStream fileStream = new FileInputStream("non_existing_file.txt");
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
FileNotFoundException
当试图打开不存在的文件时,将抛出 FileNotFoundException。它是 IOException 的一个子类,专门用于指示文件无法找到的情况。
try {
FileInputStream fileStream = new FileInputStream("non_existing_file.txt");
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}

NullPointerException
当应用程序试图在需要对象的地方使用 null 时,将抛出 NullPointerException。这是最常见的运行时异常之一,通常由于未正确初始化对象导致。
String text = null;
try {
int length = text.length();
} catch (NullPointerException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}

ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException
当数组索引超出有效范围时,将抛出 ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException。这种异常通常由逻辑错误引起,访问了数组中不存在的元素。
int[] numbers = new int[5];
try {
int value = numbers[10];
} catch (ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}

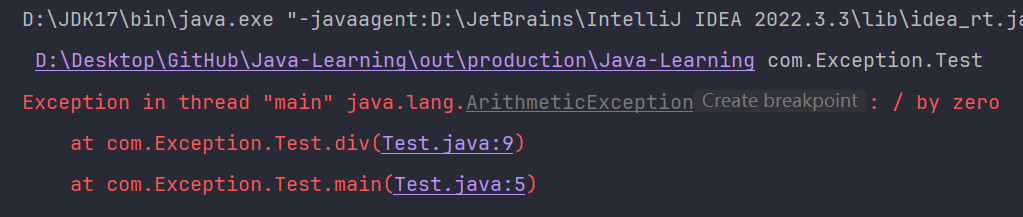
ArithmeticException
当执行算术运算时出现异常情况时,将抛出 ArithmeticException,例如,除以零。这类异常通常由数学错误引起。
try {
int result = 10 / 0;
} catch (ArithmeticException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
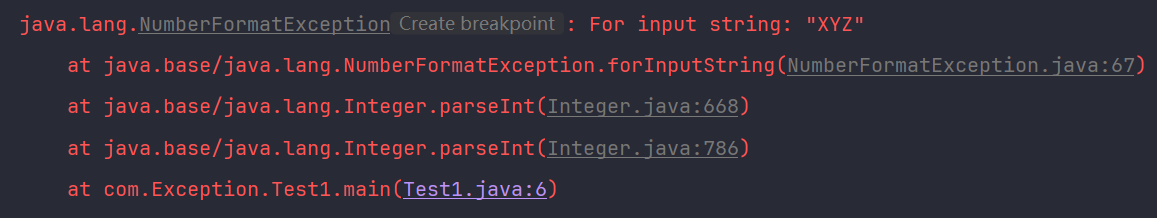
NumberFormatException
当应用程序试图将字符串转换为数值类型,但该字符串无法转换为适当的格式时,将抛出 NumberFormatException。这通常由于输入数据格式不正确导致。
try {
int number = Integer.parseInt("XYZ");
} catch (NumberFormatException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
ClassCastException
当试图将对象强制转换为不兼容的类时,将抛出 ClassCastException。这种异常通常由错误的类型转换操作引起。
Object obj = new String("hello");
try {
// 尝试将 obj(一个 String 对象)强制转换为 Integer。
// 由于 String 不能被转换为 Integer,所以这会引发 ClassCastException。
Integer number = (Integer) obj;
} catch (ClassCastException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
